NUST MISIS scientists have developed a production technology of “self-healing” asphalt-concrete materials for the road pavements.
This unique composition, which is modified with carbon nanotubes, when combinedwith the new technology used for the dissolution of roadway pavement cracks, will allow to reduce the time for the road maintenance from days to hours. Additionally, the developers have said thatthe cost of road maintenance will be at least 3 times cheaper. This technology was marked and approved by International Transportation Alliance „One Belt & On Road” (ITA) experts, and became the first international R&D project included in ITA`s program.
The new technology developed at NUST MISIS eliminates long and inconvenient replacement methods ofa roadway`s pavement, which requires extended closures of part of road lines and causes significant traffic congestion. The method involves the use of an innovative composition of „induction-healing” asphalt-concrete materials, in which a small percentage of carbon nanotubes is introduced as a modifying additive.
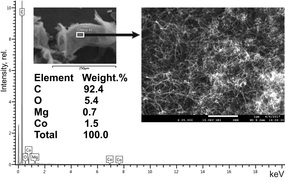
Current-conducting, multi-walled carbon nanotubes „Taunit-M” have unique parameters which determine their inductive sensitivity: a high specific surface area (about 200м2) and an external diameter of 40 nanometers, which provide the length in 1 gram of tubes that exceeds the length of Earth’s equator by ten times. That’s roughly the same length as from Earth to the Moon.
The introduction and uniform distribution of nanotubes into a viscous asphalt matrix is a complex technological challenge, yet one capable of being solved and patented only by Russian specialists.
Operating principle of „self-healing” asphalt
In the case of micro-cracks forming in asphalt after temperature changes (which is a specific problem for Russian latitudes), special mobile equipmentwitheither high-frequency induction or super-high-frequency induction is used for „healing” the cracks or balancing the road’srut. This mobile equipment quickly warms the coating layer, newly sealing it and eliminating („healing”) the defects. At this stage, the carbon nanotubes play the role of induction nano-aggregates, effectively transforming the electromagnetic radiation energy into thermal energy for the „weakening” of the coating composition.
Currently, a number of universities and technological companies from China and the Netherlands are also developing similar induction self-healing technologies, in which a metal fiber with a size of 0.5-2.5 mm is used as a modifying agent.
However, the Russian developments’ use of carbon nanotubes increases the efficiency of the method and significantly advances the capacity of the works because it involves induction heating only of the thin bitumen film covering the harder, stone materials, so it doesn’t require changes in the composition of the asphalt blend that’s requiredfor metal fiber use. Field trials of the new technology are planned for the 2017 construction season on one of the road projects implemented for the „World Cup 2018” preparations.
„The development and serial production of mobile induction units with given parameters, which are now under discussion with the ‚Rostec’ and ‚Rosatom’ corporations, is an important task for the large-scale implementation of the technology. A timely solution of this challenge will allow us to take priority not only in the Russian market but also abroad. Given that the implementation of this technology will allow for the reduction of the number of manufactured repair materials and the related anthropogenic emissions, the International Transport Alliance’s (ITA) ‚One Belt & One Road’ has approved the inclusion of an international program for the development of induction-healing materials based on this innovative technology, presented by NUST MISIS, into its technological platform for use in projects in Mongolia, Kazakhstan, Malaysia and other projects of the Silk Way. Companies from Germany, Austria, China, Hong Kong, and Malaysia, including AECOM, ASFinag, Asian Development Bank, Tianjin Hi-Tech Environment Development Co., Tongji University (Shanghai) and others have already announced their support for the program”, said Stanislav Mamulat, head of the Center for the Development of Corporate Collaboration at NUST MISIS, and an expert of the scientific-technical Council of the Federal Road Agency, „Innovations in Transport Industry” Association and International Transport Alliance (ITA) „One Belt & One Road”.
The complete package of the technology is quite complex and includes developments of several companies which complement one another: NUST MISIS, NanoTechCenter (Russia, Tambov), and Spekomiks-M. The development of the mobile HF/SHF-installations is scheduled to begin with Ruselectronics company, which belongs to the Russian State corporation „ROSTEC”.
"NUST MISIS has become the first Russian organization included in the global innovative-technological platform International Transport Alliance (ITA)"One Belt & One Road„, established by the International Road Federation, CH&TS, TRB, the Asian Development Bank, and other major global corporations in Asia and the U.S. StanislavMamulat, head of the Center for the Development of Corporate Collaboration at NUST MISIS, has become a member of the ITA expert council along with 50 other world-leading experts in the field of the transport industry. Additionally, the program of „self-healing” asphalt-concrete materials modified with carbon nanotubes, proposed by NUST MISIS scientists, has become one of the first international programs of the International Transport Alliance", said Alevtina Chernikova, Rector of NUST MISIS.